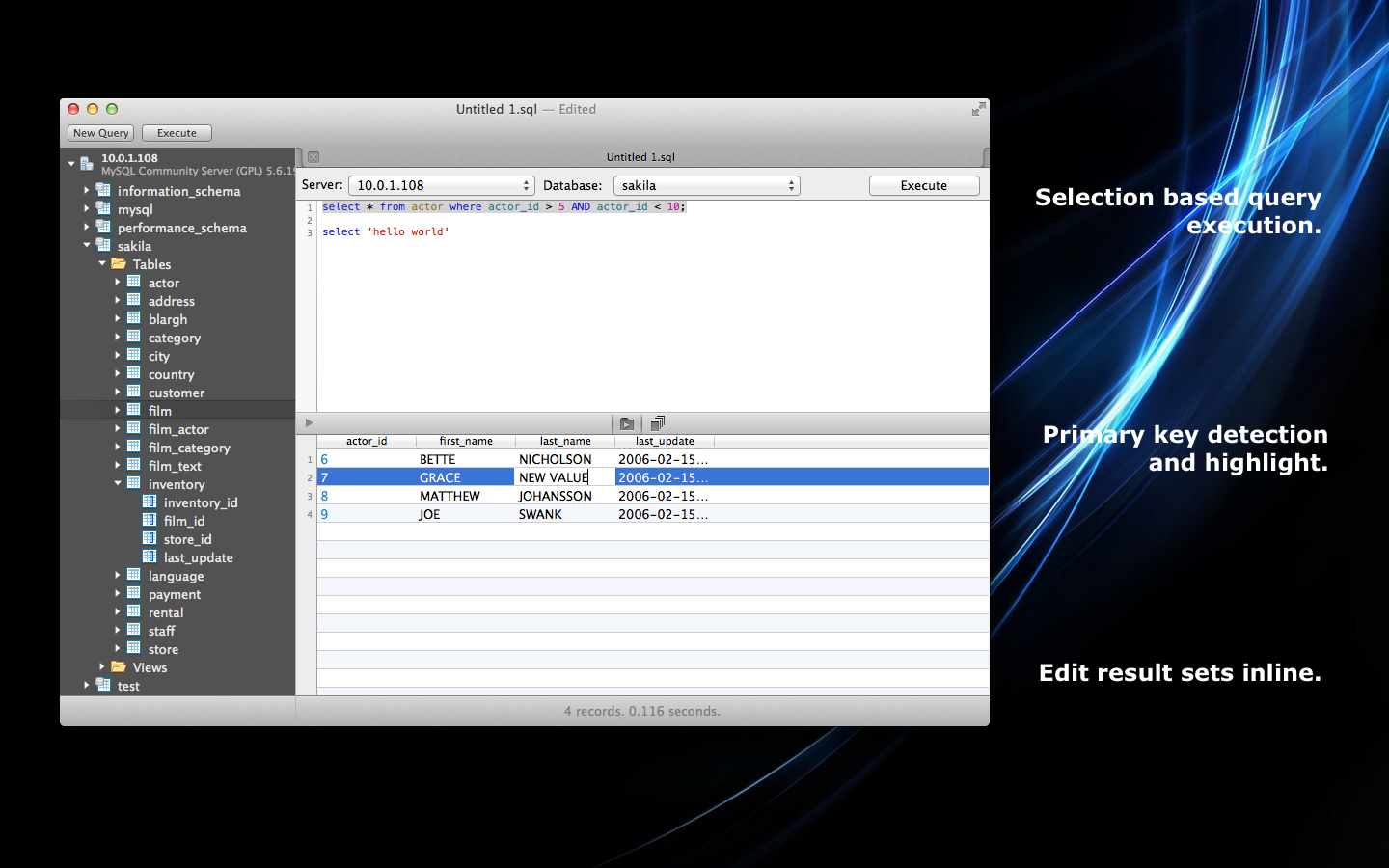
Dec 22, 2020 With SQLPro you can work simultaneously with Oracle, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, MySql and Sqlite databases. DownloadSQLProforMSSQL1019 (@downloadSQLProforMSSQL. SQLPro Studio is the premium database management tool for Postgres, MySQL, Microsoft Management Studio and Oracle databases. SQLPro supports many database types including MySQL (and MariaDB), Postgres/PostgreSQL, Redshift, Microsoft SQL Server (2005 and above), Oracle (8i and above), SQLite and SnowflakeDB.
Translation(s): English - español - Italiano - Русский
PostgreSQL, also known as Postgres, is a free and open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) emphasizing extensibility and SQL compliance.
PostgreSQL has extensive and good help that should be the first source of information regarding this database product. This page outlines main differences to generic PostgreSQL installation used by Debian.
Contents
Installation
Required packages: postgresqlpostgresql-client
Recommended packages:
postgresql-doc - PostgreSQL documentation.
phppgadmin - PostgreSQL web-based administration tool.
Please note that the procedural languages are installed separately (plpgsql comes by default). Search Debian packages to find the list of possibilities:
User access
Both the default database user and default database are called postgres. Pricewatcher 1 2 14 – monitor price changes online.
You will need administrative rights.
As root:
If your system uses sudo to get administrative rights:
New User and database
Create a regular system user account using adduser (skip this step to use an existing account):
Connect to database and create a new database user and a database:
Connect as user mypguser to new database
or, if the OS user name is not the same as the database user name:
you can also use a ~/.pgpass file
Add line for auth :
Secure the file
Now you can easily connect with
More info on the syntax can be found here : https://www.postgresql.org/docs/11/libpq-pgpass.html
Migration
Warning!
Warning this part need to be validate !! If i remember well there is a better debian way.
You can adapt and use :
https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Using_pg_upgrade_on_Ubuntu/Debian
Documentation
To get an overview about Debian's PostgreSQL architecture, instructions for a quick start, and pointers to the programs and manpages, have a look at /usr/share/doc/postgresql-common/README.Debian.gz.
Tutorial files
PostgreSQL documentation points to tutorial, which is included in the postgresql-doc package. Once the package is installed, to get more information look at /usr/share/doc/postgresql-doc-[version]/tutorial/README.
Listing existing database clusters
Use pg_lsclusters command to check installed clusters and obtain some basic information such as: version (major version), name, port, status (online or down), owner, data directory and log file.
pg_ctl replacement
pg_ctl is a PostgreSQL command line control program that can be used to control the database. Debian has made a Perl-wrapper for the pg_ctl called /usr/bin/pg_ctlcluster. Use the pg_ctlcluster whenever you need the pg_ctl. To customize the behavior check the /etc/postgresql/[version]/[cluster]/pg_ctl.conf
Debian installs SysV-init compatible (standard) start-up script /etc/init.d/postgresql-[version]. It can be used to start, stop, restart and reload the system. It calls pg_ctlcluster internally.
File locations
Both the default database user and default database are called postgres. Pricewatcher 1 2 14 – monitor price changes online.
You will need administrative rights.
As root:
If your system uses sudo to get administrative rights:
New User and database
Create a regular system user account using adduser (skip this step to use an existing account):
Connect to database and create a new database user and a database:
Connect as user mypguser to new database
or, if the OS user name is not the same as the database user name:
you can also use a ~/.pgpass file
Add line for auth :
Secure the file
Now you can easily connect with
More info on the syntax can be found here : https://www.postgresql.org/docs/11/libpq-pgpass.html
Migration
Warning!
Warning this part need to be validate !! If i remember well there is a better debian way.
You can adapt and use :
https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Using_pg_upgrade_on_Ubuntu/Debian
Documentation
To get an overview about Debian's PostgreSQL architecture, instructions for a quick start, and pointers to the programs and manpages, have a look at /usr/share/doc/postgresql-common/README.Debian.gz.
Tutorial files
PostgreSQL documentation points to tutorial, which is included in the postgresql-doc package. Once the package is installed, to get more information look at /usr/share/doc/postgresql-doc-[version]/tutorial/README.
Listing existing database clusters
Use pg_lsclusters command to check installed clusters and obtain some basic information such as: version (major version), name, port, status (online or down), owner, data directory and log file.
pg_ctl replacement
pg_ctl is a PostgreSQL command line control program that can be used to control the database. Debian has made a Perl-wrapper for the pg_ctl called /usr/bin/pg_ctlcluster. Use the pg_ctlcluster whenever you need the pg_ctl. To customize the behavior check the /etc/postgresql/[version]/[cluster]/pg_ctl.conf
Debian installs SysV-init compatible (standard) start-up script /etc/init.d/postgresql-[version]. It can be used to start, stop, restart and reload the system. It calls pg_ctlcluster internally.
File locations
Debian splits the database configuration from the database files, opposed to generic PostgreSQL installation that puts everything under same directory. Note that Debian allows multiple clusters and even different versions of PostgreSQL to co-exist in same host.
Configuration files: /etc/postgresql/[version]/[cluster]/
Binaries: /usr/lib/postgresql/[version]
Data files: /var/lib/postgresql/[version]/[cluster]
Log files: Installing PostgreSQL creates log directory /var/log/postgresql/. Starting the database engine creates log file with name postgresql-[version]-[cluster].log.
Changing Debian default installation
Debian PostgreSQL installation automatically calls initdb i.e. it initializes the cluster with default encoding and locale. To change the locale (and possibly other options in initdb), delete the existing default cluster and create a new one:
Sqlpro For Postgres 2019
Warning!
The following operation obviously deletes everything you had in cluster databases. Perform this operation right after you have installed the base package.
- Take root privileges.
- Run the following command: For example:
- Run initdb with your options. For example:
Check the Locale page to see how to add more locales.
See Also
PostgreSQL packages in Debian
DebianGis/UpdatingPostGIS (also describes upgrading postgresql)
External Links
Postgresql App
Postgresql App Windows
Official PostgreSQL web site
PostgreSQL in Debian Help web site
http://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/GUI_Database_Design_Tools
https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Design_Tools
Practical PostgreSQL
https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-add-postgresql-user-account/
Patterno 2 7 – tiled pattern and background image generator. https://www.linode.com/docs/databases/postgresql/debian-6-squeeze/
Enabling core files for PostgreSQL on Debian
http://www.debianhelp.co.uk/postgresql.htm
http://www.debianhelp.co.uk/postgresqlweb.htm
CategoryNetworkCategorySoftwareCategoryDatabase

